From the Middle Kingdom to the People's Republic: A Brief History of Asia

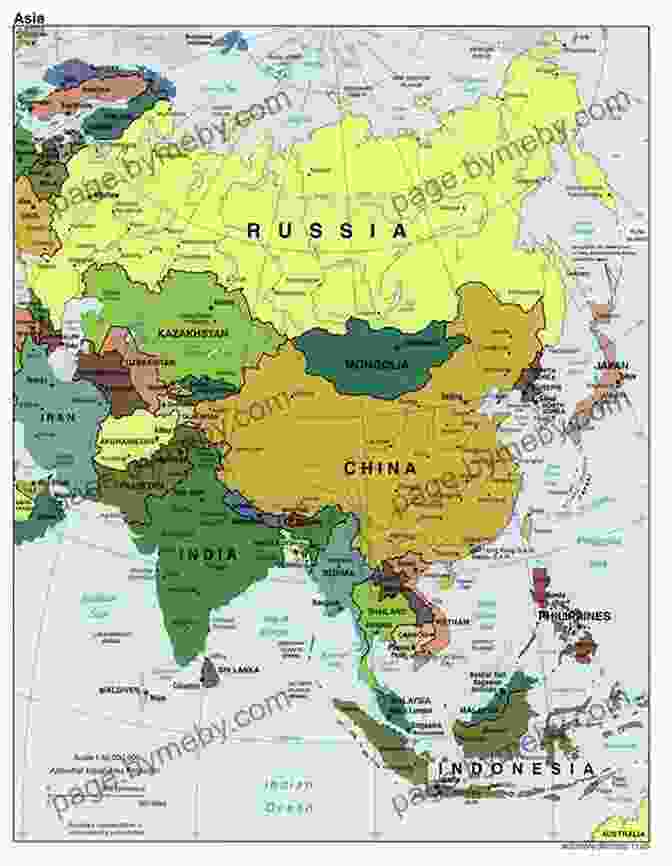
Asia is the world's largest and most populous continent, stretching from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east, and from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Indian Ocean in the south. It is home to a diverse range of cultures, religions, and languages, and has been a major center of civilization for thousands of years.
The earliest known civilizations in Asia developed in Mesopotamia and the Indus Valley around 3500 BC. These civilizations were followed by the rise of empires in China, India, and Persia. In the 15th century, European explorers began to arrive in Asia, and by the 19th century, much of the continent was under European colonial rule.
4.7 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 15655 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Word Wise | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 352 pages |
After World War II, most of Asia gained independence. However, the continent has continued to be plagued by conflict, poverty, and inequality. In recent decades, Asia has also been a major center of economic growth, and is now home to some of the world's most powerful economies.
The Middle Kingdom

The Middle Kingdom is a term used to refer to China, which was the center of a vast empire that stretched across much of East Asia for centuries. The first Chinese dynasty, the Xia dynasty, is said to have been founded in 2070 BC. The Shang dynasty, which followed the Xia dynasty, is the first Chinese dynasty for which there is確鑿的證據。The Shang dynasty was followed by the Zhou dynasty, which lasted for over 800 years and is considered to be one of the most important dynasties in Chinese history.
During the Zhou dynasty, China experienced a period of great cultural and intellectual development. The Confucian and Daoist philosophies were developed during this time, and the Chinese writing system was standardized. The Zhou dynasty also saw the rise of the first major Chinese cities, such as Beijing and Nanjing.
In the 3rd century BC, the Qin dynasty conquered the Zhou dynasty and established the first unified Chinese empire. The Qin dynasty was followed by the Han dynasty, which lasted for over 400 years and is considered to be one of the greatest dynasties in Chinese history. The Han dynasty saw the expansion of the Chinese empire into Central Asia and the establishment of the Silk Road, which connected China to the West.
The Han dynasty was followed by a period of division and civil war. In the 6th century AD, the Sui dynasty reunified China and established a new empire. The Sui dynasty was followed by the Tang dynasty, which lasted for over 300 years and is considered to be one of the most prosperous and cosmopolitan dynasties in Chinese history. The Tang dynasty saw the expansion of the Chinese empire into Korea and Japan, and the establishment of a vast trade network that stretched across Asia.
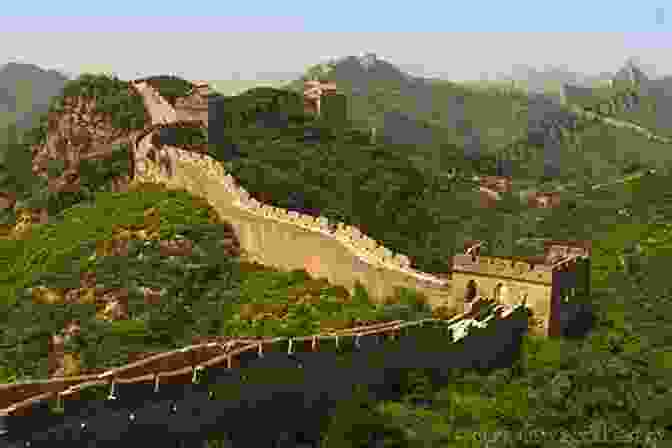
The Tang dynasty was followed by a period of decline and disunity. In the 13th century, the Mongols conquered China and established the Yuan dynasty. The Yuan dynasty was followed by the Ming dynasty, which lasted for over 300 years and is considered to be one of the most powerful and prosperous dynasties in Chinese history. The Ming dynasty saw the construction of the Great Wall of China, which is one of the most famous landmarks in the world.
The Ming dynasty was followed by the Qing dynasty, which lasted for over 200 years and is considered to be the last imperial dynasty in Chinese history. The Qing dynasty was overthrown in 1912, and China became a republic.
The People's Republic

The People's Republic of China was founded in 1949, after the Chinese Communist Party led by Mao Zedong defeated the Nationalist Party in the Chinese Civil War. Mao Zedong became the first leader of the People's Republic of China, and he ruled the country until his death in 1976.
During Mao's rule, China underwent a period of radical social and economic transformation. The land was collectivized, and private property was abolished. The government also launched a series of campaigns to suppress political opposition, including the Cultural Revolution, which lasted from 1966 to 1976.
After Mao's death, Deng Xiaoping became the leader of China. Deng Xiaoping introduced a series of economic reforms that opened up the Chinese economy to the outside world. These reforms led to a period of rapid economic growth, and China has become one of the world's leading economies.
However, the Chinese government has also been criticized for its human rights record. The government has been accused of suppressing political dissent, and of using torture and arbitrary detention. The government has also been criticized for its treatment of ethnic minorities, such as the Tibetans and the Uyghurs.
Despite these criticisms, China has made significant progress in recent decades. The country has lifted millions of people out of poverty, and it has become a major player on the world stage. China is now the world's second largest economy, and it is a permanent member of the United Nations Security Council.
A Brief History of Asia
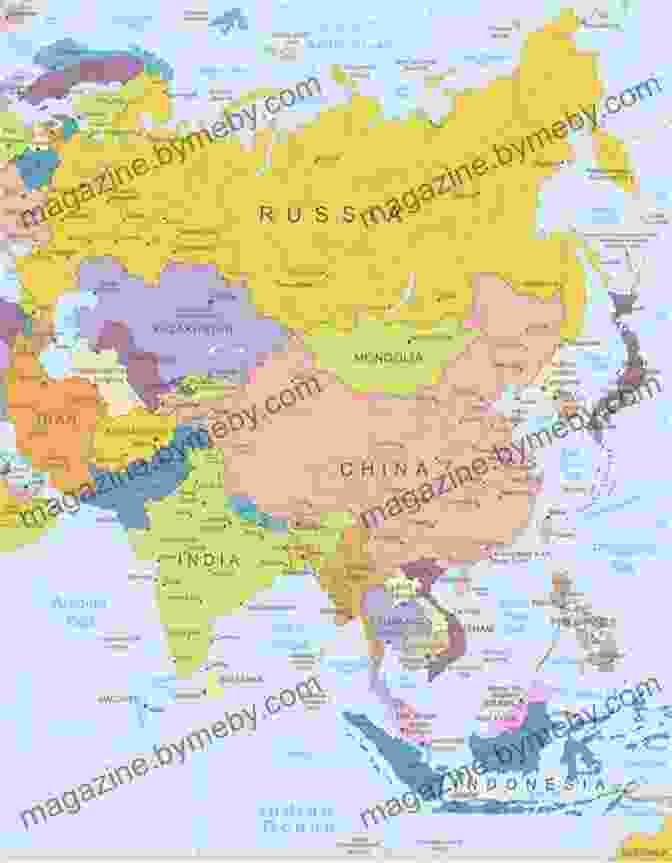
Asia is the world's largest and most populous continent, and it has a rich and diverse history. The first known civilizations in Asia developed in Mesopotamia and the Indus Valley around 3500 BC. These civilizations were followed by the rise of empires in China, India, and Persia.
In the 15th century, European explorers began to arrive in Asia, and by the
4.7 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 15655 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Word Wise | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 352 pages |
Do you want to contribute by writing guest posts on this blog?
Please contact us and send us a resume of previous articles that you have written.
 Book
Book Novel
Novel Page
Page Chapter
Chapter Text
Text Story
Story Genre
Genre Reader
Reader Library
Library Paperback
Paperback E-book
E-book Magazine
Magazine Newspaper
Newspaper Paragraph
Paragraph Sentence
Sentence Bookmark
Bookmark Shelf
Shelf Glossary
Glossary Bibliography
Bibliography Foreword
Foreword Preface
Preface Synopsis
Synopsis Annotation
Annotation Footnote
Footnote Manuscript
Manuscript Scroll
Scroll Codex
Codex Tome
Tome Bestseller
Bestseller Classics
Classics Library card
Library card Narrative
Narrative Biography
Biography Autobiography
Autobiography Memoir
Memoir Reference
Reference Encyclopedia
Encyclopedia Michael Crichton
Michael Crichton John Philip Hunter
John Philip Hunter Judith M Heimann
Judith M Heimann Tim Parks
Tim Parks Joseph D Antoni
Joseph D Antoni Thomas S Abler
Thomas S Abler Martin L Friedland
Martin L Friedland Nikki Pezzopane
Nikki Pezzopane Jonathan W Jordan
Jonathan W Jordan Johnathan Leow
Johnathan Leow Judy Bolton Fasman
Judy Bolton Fasman Julie Buxbaum
Julie Buxbaum Richard J Tofel
Richard J Tofel Tony Vanderwarker
Tony Vanderwarker John N Herbers
John N Herbers Joshua Lawrence Kinser
Joshua Lawrence Kinser Rosa Isolde Reuque Paillalef
Rosa Isolde Reuque Paillalef Richard Rodriguez
Richard Rodriguez John Romer
John Romer Thomas Poulsom
Thomas Poulsom
Light bulbAdvertise smarter! Our strategic ad space ensures maximum exposure. Reserve your spot today!

 Gabriel Garcia MarquezRediscovering the Needs of Women During Pregnancy and Childbirth: Health...
Gabriel Garcia MarquezRediscovering the Needs of Women During Pregnancy and Childbirth: Health... Marcus BellFollow ·14.6k
Marcus BellFollow ·14.6k Evan SimmonsFollow ·5.2k
Evan SimmonsFollow ·5.2k Geoffrey BlairFollow ·8.6k
Geoffrey BlairFollow ·8.6k Colin RichardsonFollow ·10.6k
Colin RichardsonFollow ·10.6k Peter CarterFollow ·14.7k
Peter CarterFollow ·14.7k Miguel de CervantesFollow ·12.1k
Miguel de CervantesFollow ·12.1k Hugo CoxFollow ·14.1k
Hugo CoxFollow ·14.1k Herman MelvilleFollow ·4.1k
Herman MelvilleFollow ·4.1k

 Efrain Powell
Efrain PowellCritical Thinker's Guide to Media Bias and Political...
In a world awash with information, it has...

 Aubrey Blair
Aubrey BlairMurder Is Bad Manners: An Unforgettable English Mystery
Prepare yourself for a captivating literary...

 Luke Blair
Luke BlairDon't Settle For Safe: Embrace Adventure and Live a Life...
<p>In this inspiring and...

 W.H. Auden
W.H. AudenRoblox Codes Dragon Adventures King Legacy All Combat...
Roblox is a massively popular online game...
4.7 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 15655 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Word Wise | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 352 pages |